KAIST Researchers develop High-Power, Fast-Charging Sodium-Ion Battery
Researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a high-energy, high-power hybrid sodium-ion battery capable of charging in seconds. This breakthrough could potentially revolutionize the energy storage industry and provide a viable alternative to lithium-ion batteries.
- Sodium is over 500 times more abundant than lithium, making it a cheaper and more accessible alternative
- Sodium-ion batteries have faced limitations such as lower power output, constrained storage properties, and longer charging times
- Developing next-generation sodium-ion batteries with improved performance is crucial for widespread adoption
About KAIST’s Hybrid Sodium-Ion Battery
- Developed by Professor Jeung Ku Kang and his team from KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering
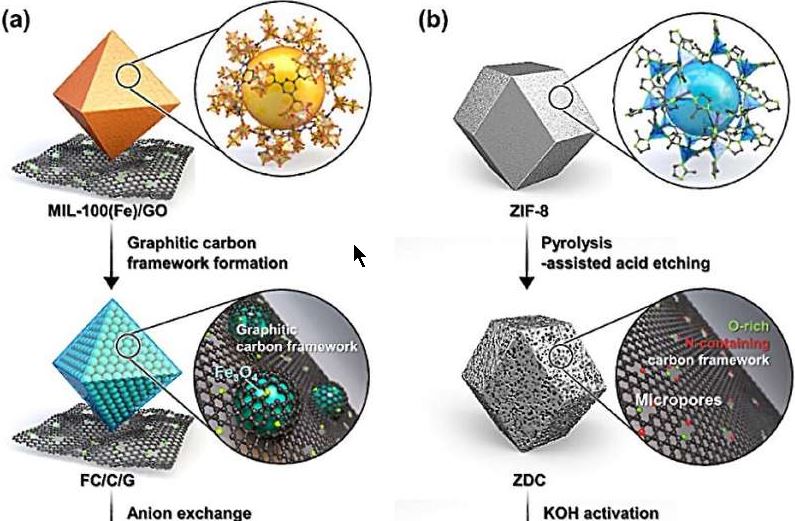
- Integrates anode materials typically used in batteries with cathodes suitable for supercapacitors
- Achieves high storage capacities and rapid charge-discharge rates
- Overcomes slow energy storage rate of battery-type anodes and low capacity of supercapacitor-type cathodes
Key Innovations
- Utilized two distinct metal-organic frameworks for optimized synthesis of hybrid batteries
- Developed anode material with improved kinetics by including fine active materials in porous carbon derived from metal-organic frameworks
- Synthesized high-capacity cathode material
- Optimized balance and minimized disparities in energy storage rates between electrodes
Performance and Potential Applications
- Assembled full cell surpasses energy density of commercial lithium-ion batteries
- Exhibits characteristics of supercapacitors’ power density
- Capable of rapid charging, achieving energy density of 247 Wh/kg and power density of 34,748 W/kg
- Anticipated to have broad applications across various electronic devices, electric vehicles, and aerospace technologies
Significance and Future Outlook
- Represents a breakthrough in overcoming current limitations of energy storage systems
- Positions sodium-ion batteries as a viable next-generation alternative to lithium-ion batteries
- Could potentially meet increasing demand for low-cost, high-performance electrochemical energy storage devices
- Further research and development needed to scale up and commercialize the technology
As the demand for sustainable energy solutions grows, advancements like this hybrid sodium-ion battery could play a crucial role in shaping the future of energy storage technology.
Month: Current Affairs - April, 2024
Category: Science & Technology Current Affairs