Climate Change and Fire Seasons
Climate change is intensifying the risk of wildfires globally. Recent studies indicate that fire weather seasons in eastern Australia and western North America are increasingly overlapping. This shift complicates international cooperation between fire services in Canada, the United States, and Australia.
About Fire Weather Conditions
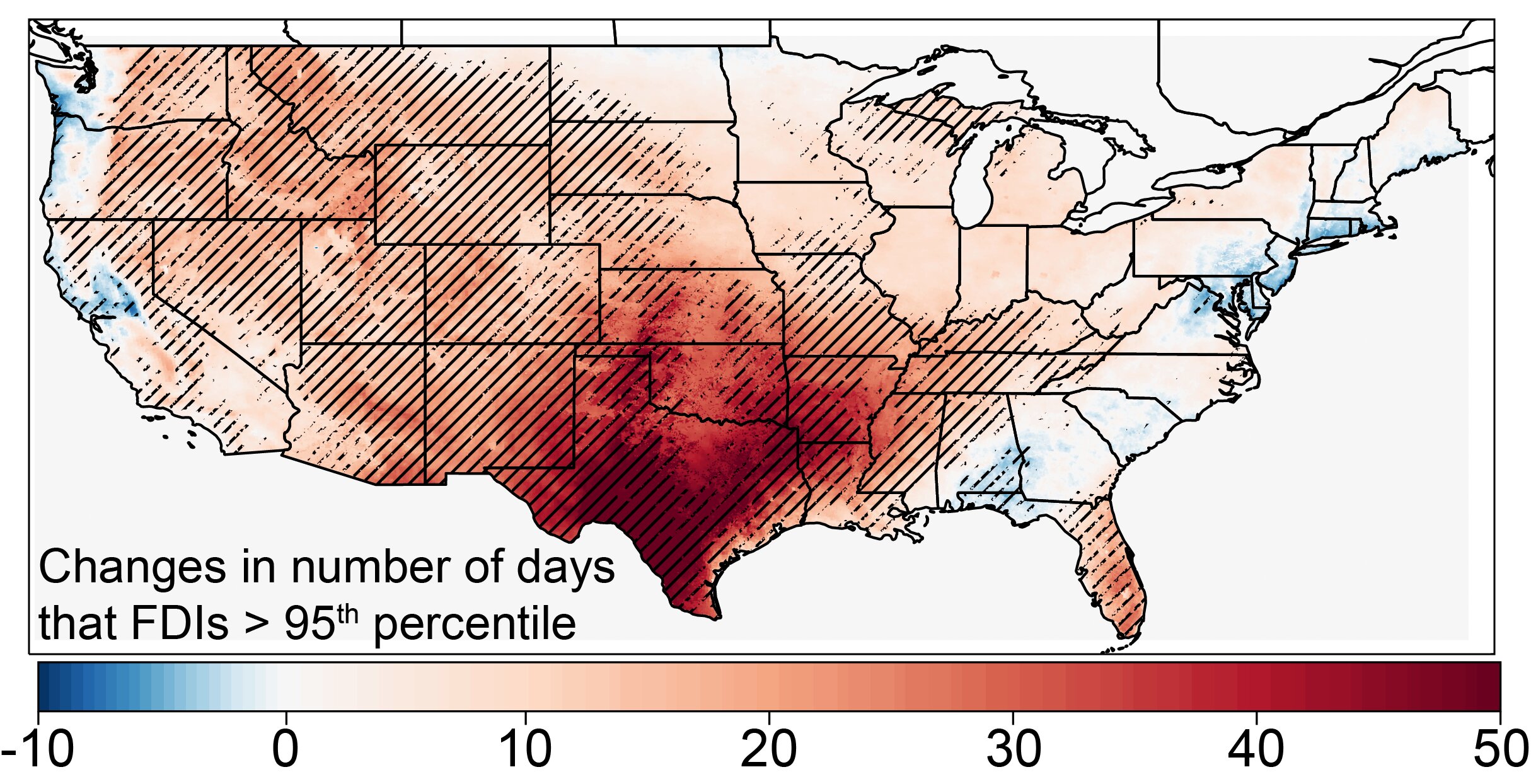
Fire weather refers to specific atmospheric conditions that promote the spread of wildfires. Key factors include temperature, humidity, rainfall, and wind speed. The Canadian Fire Weather Index (FWI) is tool used worldwide to assess fire risk. It identifies days with high wildfire potential.
Historical Context of Fire Seasons
Historically, fire seasons in western North America occurred from June to October, while eastern Australia’s season spanned from October to March. This timing allowed for resource sharing during emergencies. However, climate change is altering these patterns, leading to longer fire seasons.
Overlapping Fire Weather Days
Research shows that since 1979, the number of overlapping fire weather days has increased by one day annually. The most overlap occurs between July and December, with a 75% likelihood of simultaneous fire conditions. This trend poses challenges for cross-border firefighting efforts.
Role of El Niño and La Niña
- El Niño: Warmer Pacific Ocean temperatures → linked to droughts and fires in Australia.
- La Niña: Cooler Pacific Ocean temperatures → linked to fires in North America.
- Despite their opposite patterns, El Niño is often strong during overlapping fire seasons.
- But in the future, climate change effects will dominate over El Niño/La Niña.
Future Projections
Climate models predict that by 2050, the overlap of fire weather days could increase by 4 to 29 days per year, depending on global warming scenarios. This further convergence of fire seasons will strain international firefighting resources.
International Cooperation
- Australia, USA, and Canada share firefighting resources (personnel, aircraft, equipment).
- Earlier, their fire seasons did not clash—helping mutual aid.
- North America: June to October
- Australia: October to March
- Now, overlapping seasons are reducing the window for support and making cooperation difficult.
Recommendations for Firefighting Strategies
To address the challenges posed by overlapping fire seasons, countries should enhance their firefighting capabilities. This includes investing in equipment and training for local fire services. International agreements on resource sharing need to be revisited to adapt to the changing landscape of wildfire risks.
Month: Current Affairs - May, 2025
Category: Environment Current Affairs