Global Warming Impacts Marine Ecosystem Most: Study
According to research study conducted by Rutgers University in US and published in Journal of Nature, marine ecosystem and sea creatures are most affected by global warming. It is first research which compares cold-blooded marine and land species sensitivity to global warming and their ability of finding refuge from heat even while staying in their normal habitats.
It studied worldwide research on nearly 400 species from lizards and fish to spiders. Researchers calculated safe conditions for 88 marine and 294 land species and coolest temperatures available to each species during hottest parts of year.
Key finding
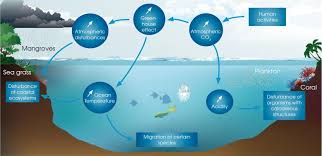
According to study, global warming can wipe out two times more ocean-dwelling species than land and dwelling species from their habitats.
Vulnerability faced by sea creatures might impact human communities relying on fish and shellfish for food and economic activity.
Loss of marine population can deplete species genetic diversity, cascade impacts on their predators and prey and can alter ecosystems that benefits human society.
Reason: It is because unlike land animals who can hide from heat in forests, shaded areas or underground, many sea animals are not open to such luxury. On average this makes marine species, more likely to live on edge of dangerously high temperatures.
Consequences: Loss of population can deplete species’ genetic diversity, have cascading impacts on their predators and prey and may significantly impact human communities that rely on fish and shellfish for food and economic activity.
Way Forward
If oceans will continue supporting human well-being, nutrition and economic activity, then new conservation efforts and more research will be required. Also, with advancement of climate change, it is important to develop understanding about which species and ecosystems will be most severely affected by global warming, as it will further guide conservation and management efforts.
Marine Ecosystem
They are Earth’s largest aquatic ecosystems and are most prevalent out of all types of ecosystems on planet. They have a high salt content in contrast with freshwater ecosystems, which have lower salt content. They are filled with life, provide nearly half of Earth’s oxygen and are home to wide varieties of species.
Month: Current Affairs - April, 2019